Ardennes
| Ardennes | |
|---|---|
 Landscape of Frahan inside the bend of the Semois River |
|
|
|
|
| Location | Wallonia, Belgium Luxembourg Ardennes département and Champagne-Ardenne, France |
| Area | 11,200 km2 (2,768,000 acres) |
| Governing body | Parc National de Champagne/Ardennes Parc National de Furfooz |
The Ardennes (pronounced /ɑrˈdɛn/; Dutch: Ardennen) is a region of extensive forests, rolling hills and ridges formed within the Givetian (Devonian) Ardennes mountain range[1], primarily in Belgium and Luxembourg, but stretching into France (lending its name to the Ardennes département and the Champagne-Ardenne région), and geologically into the Eifel. In Wallonia, the word 'Ardenne' in the singular is commonly used for the Belgian part of the region and in the plural for the French one. Ardenne is the origin of the great industrial period of Wallonia, the second of the world (18th, 19th and 20th centuries). In France, the word 'Ardennes' in the plural, together with the definite article, is commonly used to refer to the French Department of that name.
Contents |
Geography
Much of the Ardennes is covered in dense forests, with the mountains averaging around 350-500 m (1,148-1,640 ft) in height but rising to over 650 m (2,132 ft) in the boggy moors of the Hautes Fagnes (Hohes Venn) region of north-eastern Belgium. The region is typified by steep-sided valleys carved by swift-flowing rivers, the most prominent of which is the Meuse. Its most populous cities are Verviers in Belgium and Charleville-Mézières in France, both exceeding 50,000 inhabitants. The Ardennes is otherwise relatively sparsely populated, with few of the cities exceeding 10,000 inhabitants with a few exceptions like Eupen or Bastogne.
The Eifel range in Germany adjoins the Ardennes and is part of the same geological formation, although they are conventionally regarded as being two distinct areas.
Geology
L' Ardenne (Wallonian spelling), is an old mountain formed during the Hercynian orogeny as for instance in France the Armorican Massif, the Massif Central and the Vosges. At the bottom of these old mountains, coal, iron, zinc, and other metals are often found in the sub-soil. This geologic fact explains the greatest part of the geography of Wallonia and its history. In the North and West of the Ardennes lie the valleys of the Sambre and Meuse rivers, forming an arc Sillon industriel going across the most industrial provinces of Wallonia, for example Hainaut, along the river Haine (the etymology of Hainaut) : the Borinage, the Centre and Charleroi along the river Sambre, Liège along the river Meuse.
This geological region is also very important in the history of Wallonia because this old mountain is at the origin of the economy, the history, and the geography of Wallonia. "Wallonia presents a wide range of rocks of various ages. Some geological stages internationally recognized were defined from rock sites located in Wallonia : e.g. Frasnian (Frasnes), Famennian (Famenne), Tournaisian (Tournai), Visean (Visé), Dinantian (Dinant) and Namurian (Namur)"[2] The Tournaisian excepted, all these rocks are in the Ardennes viewed as a geological area.
Economy
The Ardennes includes the greatest part of the province of Luxembourg (number 4), the south of the province of Namur (number 5) and the province of Liège (number 3), and a very small part of Hainaut (number 2). There were the first furnaces in the four Walloon provinces, using, before the 18th century, charcoal which was made in the Ardennes forest. This industry was also in the extreme South of the Luxembourg, in the region called Gaume. After this century, the most important part of the Walloon steel industry, using then coal, was built around the coal-mines, principally in the region around the cities of Liège, Charleroi, La Louvière, the Borinage, and further in the Walloon Brabant (in Tubize). Wallonia became the second industrial power of the world in proportion to its territory and to its population (see further).
The rugged terrain of the Ardennes severely limits the scope for agriculture, with arable and dairy farming in cleared areas the mainstay of the agricultural economy. The region is rich in timber and minerals, and Liège and Namur are both major industrial centres. The extensive forests have an abundant population of wild game. The scenic beauty of the region and its wide variety of outdoor activities, including hunting, cycling, walking and canoeing, make it a popular tourist destination.
History
The region took its name from the ancient Arduenna Silva, a vast forest in Roman times, that stretched from the Sambre river in Belgium to the Rhine in Germany. The forest was named after a pagan goddess Arduinna. The modern Ardennes covers a much smaller area.
In The Song of Roland, Charlemagne had a nightmare the night before the Battle of Roncevaux Pass. This nightmare took place in the Ardennes' forest where he had his most important battles.
Wallonia has plenty of rivers, villages and other places linked to another song about Charlemagne: the Old French twelfth century chanson de geste Quatre Fils Aymon. One of these places, in Dinant, is the rock named Bayard. This rock was named for the magic bay horse which, according to the legend, jumped from the top of the rock to as far as the other bank of the Meuse.
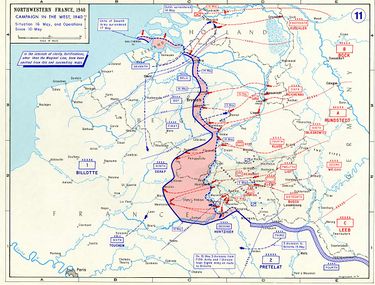
The highly strategic position of the Ardennes has made it a battleground for European powers for centuries. The region repeatedly changed hands during the early modern period, with parts or all of the Belgian Ardennes being incorporated into France, Germany, the Spanish Netherlands, the Austrian Netherlands and the United Kingdom of the Netherlands at various times. In the 20th century, the Ardennes was widely thought unsuitable for large-scale military operations due to its difficult terrain and narrow lines of communications. However, in both World War I and World War II, Germany successfully gambled on making a rapid passage through the Ardennes to attack a relatively lightly defended part of France. The Ardennes saw three major battles during the world wars – the Battle of the Ardennes in World War I, and the Battle of France and Battle of the Bulge in World War II. Many of the towns of the region were badly damaged during the two world wars.
World War II
The Ardennes is well known because of the Battle of the Bulge, when the German Army launched a surprise attack in December 1944 in an attempt to capture Antwerp and drive a wedge between the British and American forces in northern France.
The furthest west that German troops reached during the Battle of the Bulge was not far from the town of Dinant, along the river Meuse. In May 1940, the German army was able to go across the Meuse, despite the resistance of the French army, not further than Dinant in Houx (Wallonia) (as well as in Sedan). On the command of General Erwin Rommel, the German armoured divisions were also able to go across the river in a neighbourhood of Dinant named Leffe (as the Abbey beer linked to this abbey in this neighbourhood).
In December 1944, the German army could not go across the river. Local residents say that a German vehicle exploded just before the Bayard rock, possibly when it triggered a mine laid by American soldiers, and that this is following this legend. Dinant's Rock was thus perhaps the most advanced position of the German army during this battle.
1940

1944

.jpg)

References
Notes
- ↑ p.16, Gerrard
- ↑ The origin of the geological terms are indicated by the editor Most beautiful rocks of Wallonia
Sources
- Gerrard, John, Mountain Environments: An Examination of the Physical Geography of Mountains, MIT Press, 1990